Representing Point Clouds with Generative Conditional Invertible Flow Networks
Jul 17, 2021· ,,,,·
0 min read
,,,,·
0 min read
Michał Stypułkowski
Kacper Kania
Maciej Zamorski
Maciej Zięba
Tomasz Trzciński
Jan Chorowski
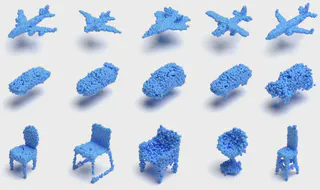 Samples generated with the proposed normalizing flow
Samples generated with the proposed normalizing flowAbstract
In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective method to represent point clouds as sets of samples drawn from a cloud-specific probability distribution. This interpretation matches intrinsic characteristics of point clouds: the number of points and their ordering within a cloud is not important as all points are drawn from the proximity of the object boundary. We postulate to represent each cloud as a parameterized probability distribution of points in space, which is defined by a generative neural network. The network operates by composing several spatial transformations of point locations. Once trained, it provides a natural framework for point cloud manipulation. For instance we can decouple cloud shape from its orientation and provide routines for aligning a new cloud into a default spatial orientation. To exploit similarities between same-class objects and to improve model performance, we turn to weight sharing: networks that model densities of points belonging to objects in the same family share all parameters with the exception of a small, object-specific embedding vector. We show that these embedding vectors capture semantic relationships between objects. Our method leverages generative invertible flow networks to learn embeddings as well as to generate point clouds. Thanks to this formulation and contrary to similar approaches, we are able to train our model in an end-to-end fashion. As a result, our model offers competitive or superior quantitative results on benchmark datasets, while enabling unprecedented capabilities to perform cloud manipulation tasks, such as point cloud registration and regeneration, by a generative network.
Type
Publication
In Pattern Recognition Letters vol. 150, pp 26-32